Cyber attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and damaging, and among the most common and devastating is DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service). This type of attack has the power to paralyze websites, online services and even entire networks, compromising the security and trust of companies and users.
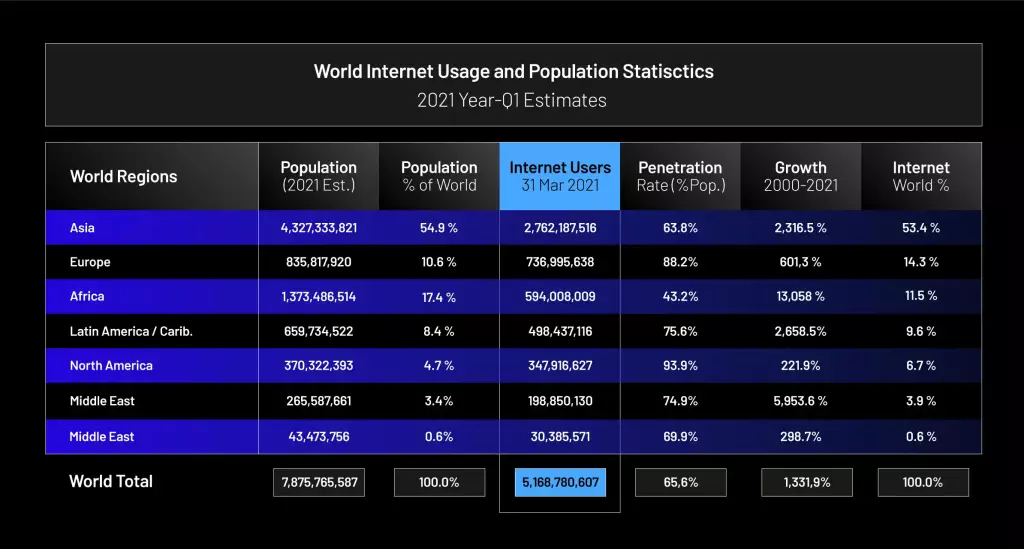
These attacks are becoming more widespread precisely because there are billions of devices connected to the Internet. What’s more, the number of users worldwide is growing every year. According to a survey carried out by Internet World Stats, at least 67% of the world’s population is connected to the internet. In other words, we are living in a time when the internet covers more than half of the entire planet.
In this sense, what we used to see only in movies – self-driving cars, holograms, artificial intelligence, etc. – is no longer so far out of our reach. Therefore, it is clear that the growth of the internet can bring security demands to be resolved, after all, technological advances have also benefited criminals.
After all, what is DDoS?
DDoS(Distributed Denial of Service ) is a well-known type of cybercrime in the world of cybersecurity.
Here, a central office controls thousands of machines and manages a large-scale attack. O cracker invades or develops its own control center (C&C) and then infects thousands of other devices with a malware virus. This group of infected machines is known as a botnet.
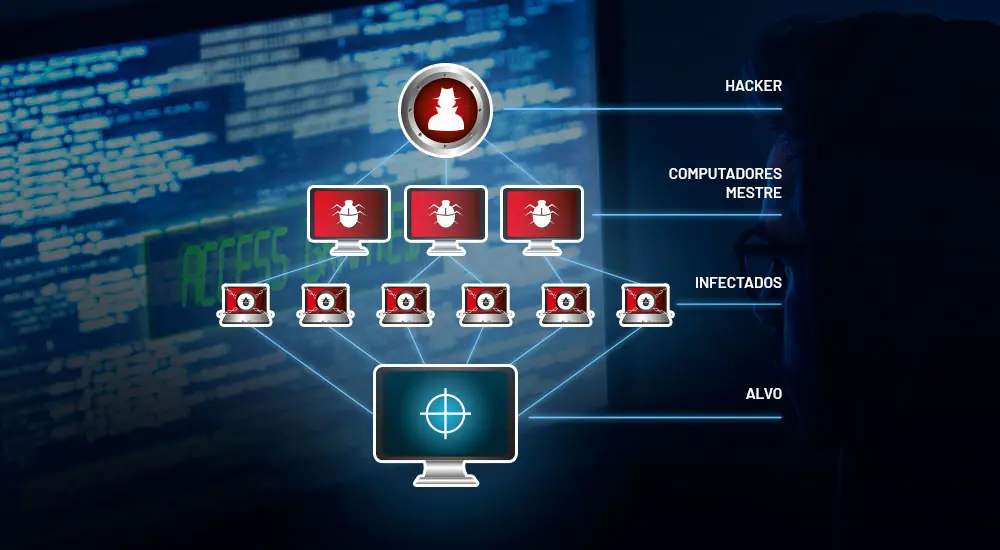
To illustrate, we can make an analogy with a zombie apocalypse. After all, the way they both multiply is very similar. If you’ve ever watched a movie or series on the subject, you’ll have noticed that the virus multiplies as the zombies infect other people.
When the number of infected people grows, the resources needed for human survival start to become scarce and inaccessible in many cases. DDoS behaves in the same way on the Internet. The infected machines consume the victims’ resources so that there is nothing else to turn to.
Finally, the main aim of DDoS attacks is to overwhelm the victim with a large amount of malicious traffic. Criminals can direct these attacks at a website, server or even an entire infrastructure. For companies, the downtime caused by DDoS causes, in addition to financial losses, damage to brand reputation, legal problems and more.
OSI model: the layers used by cybercriminals in DDoS attacks
The acronym OSI stands for Open Systems Interconnection Model and is one of the ISO(International Organization for Standardization) reference models for Internet communication protocols. The layers of the OSI model are the paths used by the attacker to carry out DDoS attacks.
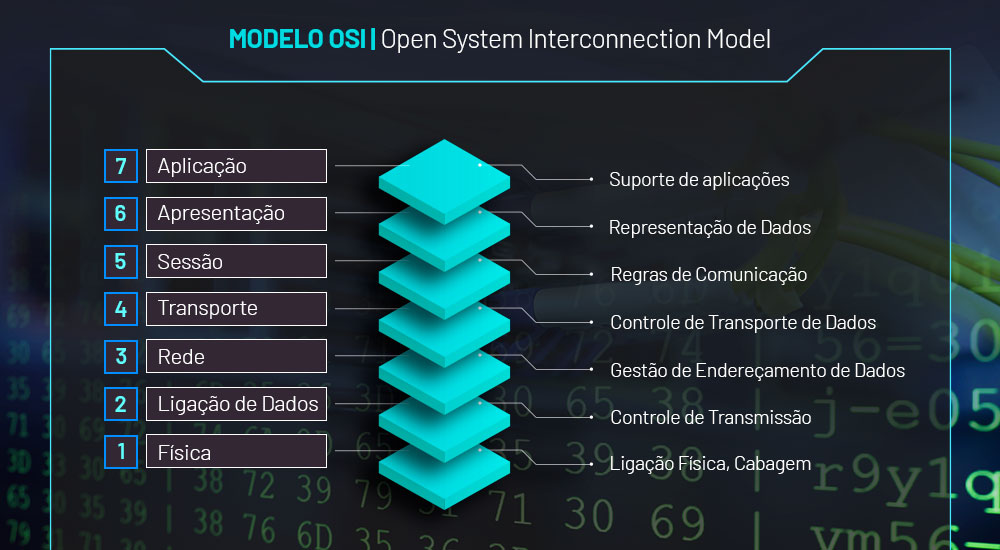
Currently, the 7 layers of the OSI Model are divided into: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation and Application.
Take a look at each one:
1 – Physical Layer
It is the base layer of the OSI model, where the physical part of the network is located. It is also responsible for transmitting raw bits on a communication channel.
2 – Data Link Layer
Layer responsible for facilitating communication between network devices. It also has the role of detecting and correcting errors found in layer 1.
3 – Network Layer
It is responsible for receiving and delivering information (data) to network recipients.
4 – Transport Layer
Responsible for summarizing data. Layer 4 is based on the TCP/IP protocol.
5 – Session Layer
Dynamically opens and closes transmissions. It creates restore points and helps with functional communication between network devices.
6 – Presentation Layer
Stage in which data is encrypted and decrypted. In addition to delivering simplified information to the application layer.
7 – Application Layer
The point at which the user has direct experience of the OSI model. This is where the interaction between people and internet-connected devices takes place.
What are the types of DDoS attacks?
There are three types of DDoS attacks: volumetric, application layer and protocol-driven. In each case, criminals apply different methods and techniques, precisely in order to exploit their target to the maximum.
Learn about the three types:
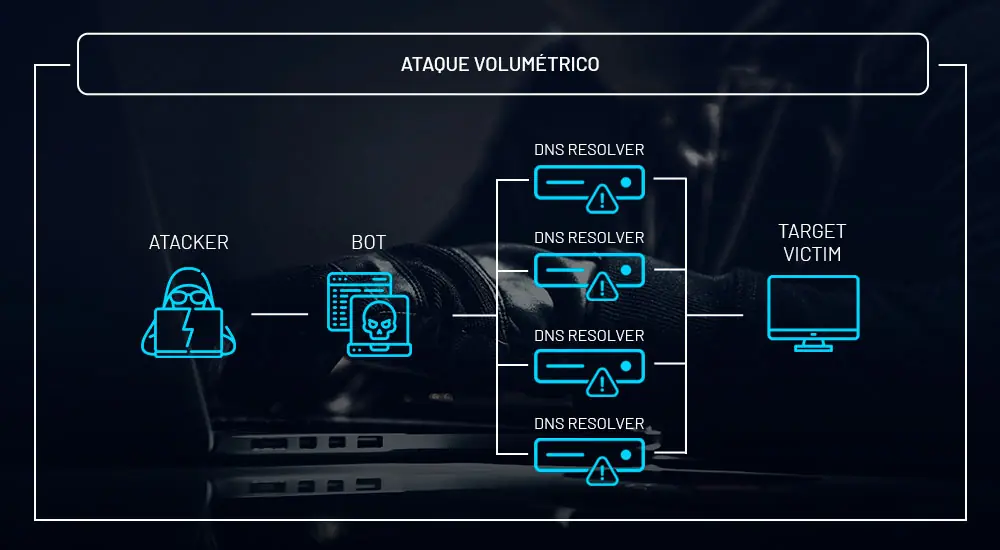
Volumetric attacks
Above all, the aim here is to consume bandwidth – internet capacity -, network and/or target service. In this sense, the idea is to overload the victim so that they are unable to communicate with the rest of the Internet. Currently, criminals benefit from the use of botnets, which are nothing more than systems and devices infected by malware under the attacker’s control.
It’s important to note that most users who are part of botnets don’t even know about it. The victim is not warned that their system or device has been hacked. In other words, everything is done without warning or signposting.
At the other end of the spectrum, we have large organizations – which are frequent victims of these attacks. However, unlike the user, companies quickly notice the symptoms and consequently the damage caused by this type of crime.
For example, imagine that an attack like this is directed at an investment app, and suddenly the platform’s investors can no longer access it. For a regular investor, this could result in significant financial losses.
And make no mistake! Cybercriminals are everywhere, just as they are willing to attack anyone who finds themselves vulnerable on the Internet. If the victim is not prepared to deal with this scenario, they will certainly be an easy target for attackers.
In addition, many of these attacks can be carried out through amplification vulnerabilities, such as DNS amplification, SSDP amplification, LDAP/CLDAP, etc.
Application layer attacks
Above all, attacks on the application layer are the most complex to mitigate. This is because the attacker sends many simultaneous requests, simulating the legitimate traffic of the target application. To illustrate, think of 1,000,000 users trying to open your website, sending lots of HTTP GET or HTTP POST requests.
Imagine thousands of Chrome tabs open and all of them simultaneously accessing the same website. In practice, this is how an attack on the application layer works. However, the number of hits is extremely high, so the victim’s application ends up being damaged.
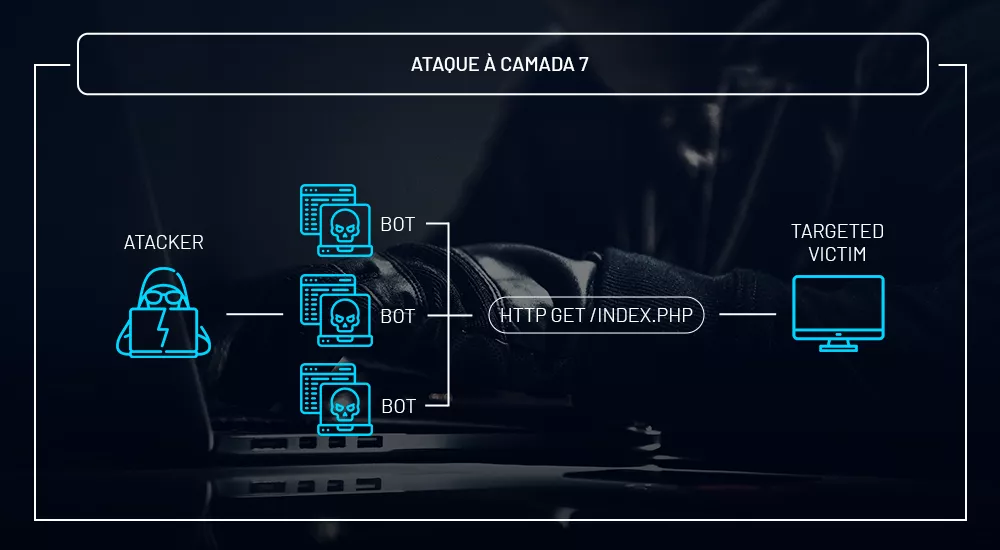
Unlike volumetric attacks that target the entire network, DDoS at layer 7 – the application layer of the OSI model – aims to interrupt a specific application of the victim.
Furthermore, when targeting layer 7, DDoS can only be mitigated through complex methodologies such as Challenge DNS, TCP SYN Proxy, Captchas, among others. However, it is worth noting that most of these attacks are low-bandwidth(bits/megabits).
However, they are highly destructive and therefore the most difficult to detect and mitigate.
Exhaustive attacks (TCP or similar)
Exhaustive TCP –Transmission Control Protocol – attacks are carried out with the aim of consuming all available hardware and processing resources, such as the CPU. In this way, through a high volume of consecutive attempts to open connections, this technique causes the target server or network to respond disproportionately.
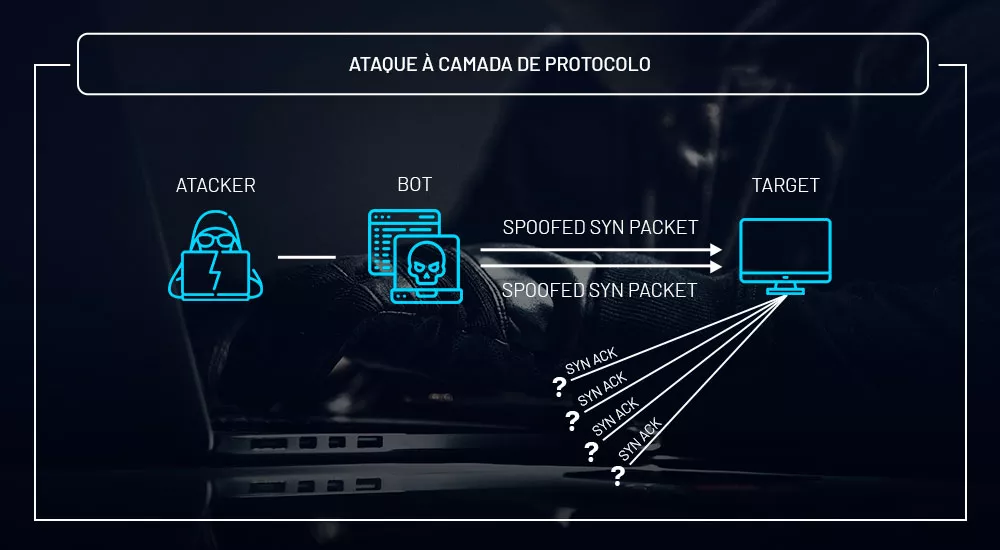
Therefore, firewalls, load balancers, routers and other high-capacity equipment can be brought down using these methods. In addition, there are other vectors explored here, such as TCP SYN, TCP SYN+ACK, TCP RST, TCP ACK, among others.
Here are the main reasons behind DDoS attacks
DDoS is a type of cyberattack that has been gaining popularity due to the damage it has caused to large companies in the market and around the world. For example, in 2015, the series Mr. Robot made headlines by tackling the issue on television around the world.

However, despite the fact that the subject has often been romanticized, the production manages to explore the universe of cybersecurity very well. The series also shows some of the main motivations behind these attacks.
There are several reasons why these crimes happen and we’ve brought some of them to you in this article:
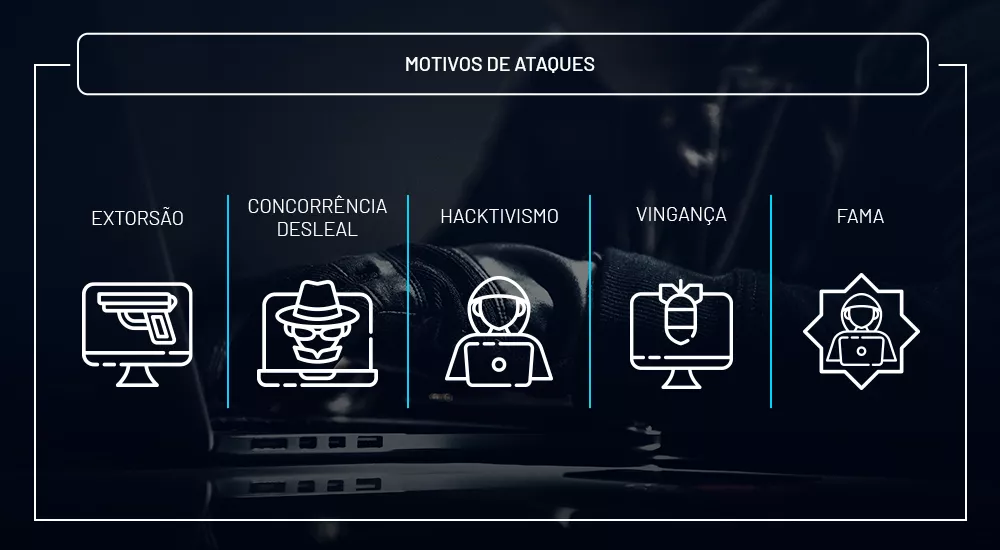
Extortion
The server or infrastructure is overloaded and taken over by the attacker. Therefore, in order to get the system back online, the criminal asks for a sum of money in return. However, there is no guarantee that the promise will actually be kept. After all, you’re dealing with a criminal.
ATTENTION! We always recommend that you do not pay any ransom for cyber attacks, as there is no guarantee. In addition, paying the ransom strengthens the striker.
Unfair competition
In order to gain a competitive edge, some companies use DDoS as a weapon to hit their competitors. Unfortunately, this practice has become very common in the market, especially in the ISP (Internet Access Provider) segment or, as they are popularly known, Internet Service Providers.
So be aware of the possible reasons why you could be suffering this attack. After all, there is the possibility of being an unfair competitor.
Hacktivism
Here, the individual uses DDoS as a means of expressing their outrage at politics, the private sector or a game server, for example. This practice is often directed at government bodies as a kind of protest against their actions. Therefore, the attack is a way of showing this dissatisfaction with the service provided.
Revenge
Another very common motivator is the “exchanged lead” between ex-employees and companies. Several scandals have already come to light about former employees who hired a DDoS attack service on the black market to get back at the company that fired them. Can you believe it?
Fame
If you’re on Twitter, you’ve probably come across a trend involving hacker groups. This is because people take a superficial view of cases involving cyber attacks. What criminals want are a few minutes of fame to promote themselves through popular causes.
So far, we’ve seen what DDoS is and why it happens so often. But the big question is: how can you protect your company, website or server from this kind of threat? Are you prepared to answer this question? No? So let’s get on with it!
How can you be protected against a DDoS attack?
Protecting yourself from a distributed denial of service attack can be a somewhat complex task. Here at Huge Networks, for example, we have a team made up of specialists from different areas, such as IT engineers, network analysts, developers and programmers. In addition, we have our own technology and a robust infrastructure that connects to the world’s main connectivity points.
However, before looking for any solution, you need to understand what your needs are when it comes to securing your network infrastructure – this will enable you to make the best decisions.
There are some resources and tools that can be used in the fight against DDoS attacks. If you manage your own network, we’re going to give you some tips to increase the security of your infrastructure and identify possible attacks.
Know your traffic
First of all, it’s very important to know your network traffic well. If you manage your own server, it is crucial that you are able to identify changes in access patterns. After all, DDoS attacks behave aggressively through a large volume of malicious traffic.
Therefore, identifying these changes is fundamental to the functioning of the infrastructure, as well as its safety.
Edge router does not mitigate DDoS attacks
Some companies entrust the entire security of their network to edge routers. However, the equipment is not designed to mitigate DDoS, but rather to handle the traffic that passes through the infrastructure in the best possible way.
Criminals can discover the fragility of your network and exploit the equipment’s vulnerabilities. The attacker can, for example, exploit different types of vectors, such as DNS amplification, SSDP amplification, etc.
DDoS attacks are always evolving and every year there is a significant increase in the number of anomalies detected and mitigated on the Internet. What’s more, criminals are always on the lookout for new technologies to improve their techniques.
Even if you create rules on your edge router, your infrastructure can still be a target – after all, the equipment wasn’t developed for the purpose of mitigating attacks. Therefore, apply other prevention techniques and methods to make your company more secure.
Investing in bandwidth can alleviate the problem
DDoS consumes bandwidth and can easily cause your infrastructure to become saturated. So it’s only fair to invest in this feature to prevent your network from being overloaded – even in the case of minor attacks.
However, it is important to emphasize that this is only a way of softening the impact of the problem, not solving it.
Blackhole
This technique is generally used as a last resort, or when there is no other way to mitigate attacks. Although it is a way of defending yourself, blackhole (or blackholing) discards all traffic arriving on the network, meaning that both legitimate and malicious traffic will be routed to a “black hole”.
In addition, there are many problems with using this feature and the main one is that even legitimate users can be denied access to the service. You don’t want your customers to leave your site frustrated, do you?
Create rules for routers and firewalls
A basic and also very important task is to create rules on the network firewall and ACLs – access control lists – on the routers. You could, for example, configure your router to block DNS requests with UDP protocols on port 53 – this could help defend against a DNS amplification attack.
However, as mentioned in the topic on edge routers, these basic configurations are not always enough to be 100% protected against more complex DDoS attacks.
Have a mitigation specialist at your side
The techniques we have presented may not be enough to solve 100% of the problem. After all, criminals seek to exploit their victims’ infrastructure as much as possible. The ideal is to rely on a specialized solution to avoid major problems and, above all, the headaches caused by these attacks.
The mitigation solutions available today rely on cutting-edge technology and robust infrastructures to deal resiliently with DDoS attacks. By entrusting this task to a specialized company, you save financial, human and other resources necessary for your internet security.
Discover the Huge Networks solution
Today, Huge Networks has one of the most modern solutions on the market, as well as a robust and complete infrastructure to serve your company.
With proprietary technology, our DDoS protection is built on Artificial Intelligence and the latest developments in the cybersecurity market.
In addition, the solution has a methodology called “based learning” which detects all anomalies, including those unknown to the system through an intelligent learning method.
There are more than 15 points of presence at your disposal, a mitigation SLA of less than 5 seconds, 24/7 support, a dashboard for real-time monitoring and much more.
This content was produced by Huge Networks. Our company protects your corporate network, accelerates cloud applications, mitigates DDoS attacks and keeps cyber threats at bay. Subscribe to our newsletter and stay up to date with the latest news on security and digital infrastructure!
